Barbituric acid
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3-Diazinane-2,4,6-trione | |||
Other names
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 3DMet | |||
| 120502 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.598 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 101571 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C4H4N2O3 | |||
| Molar mass | 128.087 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White crystals | ||
| Melting point | 245 °C (473 °F; 518 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 260 °C (500 °F; 533 K) | ||
| 142 g/L (20 °C) | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.01 (H2O)[1] | ||
| |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||

| |||
| Warning | |||
| H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Barbituric acid or malonylurea or 6-hydroxyuracil is an organic compound based on a pyrimidine heterocyclic skeleton. It is an odorless powder soluble in water. Barbituric acid is the parent compound of barbiturate drugs, although barbituric acid itself is not pharmacologically active. The compound was first synthesised by Adolf von Baeyer.
Naming
[edit]It remains unclear why Baeyer chose to name the compound that he discovered "barbituric acid". In his textbook Organic Chemistry, the American organic chemist Louis Frederick Fieser (1899–1977) initially speculated that the name stemmed from the German word Schlüsselbart (literally, the beard (Bart, Latin: barba) of a key (Schlüssel), that is, the bit of a key), because Baeyer had regarded barbituric acid as central (or "key") to understanding uric acid and its derivatives. However, Fieser subsequently decided that Baeyer had named the compound after a young lady whom he had met and who was called "Barbara"' hence the name "barbituric acid" was a combination of the name "Barbara" and "uric acid".[2][3][4] Other sources claim that Baeyer named the compound after Saint Barbara, either because he discovered it on the feast day of St. Barbara (December 4) or because he sometimes lunched with artillery officers and St. Barbara is their patron saint.[5][6]
Synthesis
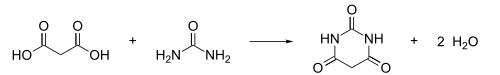
[edit]Barbituric acid was first prepared and named in 1864 by the German chemist Adolf von Baeyer, by reducing what Baeyer called Alloxanbromid (alloxan dibromide, now: 5,5-dibromobarbituric acid) with hydrocyanic acid,[7] and later by reducing dibromobarbituric acid with a combination of sodium amalgam and hydrogen iodide.[8] In 1879, the French chemist Édouard Grimaux synthesized barbituric acid from malonic acid, urea, and phosphorus oxychloride (POCl3).[9] Malonic acid has since been replaced by diethyl malonate,[10][11] because using the ester avoids the problem of having to deal with the acidity of the carboxylic acid and its unreactive carboxylate.
Properties
[edit]The α-carbon has a reactive hydrogen atom and is quite acidic (pKa = 4.01) even for a diketone species (cf. dimedone with pKa 5.23 and acetylacetone with pKa 8.95) because of the additional aromatic stabilization of the carbanion.
Uses
[edit]Using the Knoevenagel condensation reaction, barbituric acid can form a large variety of barbiturate drugs that behave as central nervous system depressants. As of 2007, more than 2550 barbiturates and related compounds have been synthesised, with 50 to 55 in clinical use around the world at present. The first to be used in medicine was barbital (Veronal) starting in 1903, and the second, phenobarbital was first marketed in 1912.[12]
Barbituric acid is a chemical building block in the laboratory synthesis of riboflavin (vitamin B2) and in a method of producing the pharmaceutical drug minoxidil.[13] It is one of the four ingredients in the synthesis of riboflavin. Before barbituric acid was substituted in the synthesis of riboflavin, it was too expensive to synthesize riboflavin.
Health and safety
[edit]Overdose of barbiturate drugs can cause respiratory depression and death.[14][15][16][17] Barbiturates are dependence-producing, and abrupt cessation of high doses can result in a very medically serious, even lethal, withdrawal syndrome. Barbituric acid derivatives are considered DEA Schedule III controlled substances.[18]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Haynes, William M., ed. (2016). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (97th ed.). CRC Press. pp. 5–89. ISBN 978-1498754286.
- ^ Levi, Leo (1957) "The barbituric acids, their chemical structure, synthesis and nomenclature," United Nations: Office on Drugs and Crime.
- ^ Fiesler, L. F., Organic Chemistry (Boston, Massachusetts: D.C. Heath and Company, 1944), p. 247.
- ^ See also:
- Willstätter, Richard Martin, Aus meinen Leben: von Arbeit, Musse und Freunden [From my life: of work, leisure and friends] (Weinheim, Germany: Arthur Stoll, 1949). English translation: Willstätter, R. with L. S. Hornig, trans., From My Life: The Memoirs of Richard Willstätter (New York, New York: W. A. Benjamin, 1965), "Memories of Adolf von Baeyer," p. 119.
- Cohen, W. A. T. (1943) "Chemisch-Historische Aanteekenigen: De nomenclatur van enkele organische zuren" (Chemical-historical notes: the nomenclature of some organic acids), Chemisch Weekblad, 40: 176.
- Kauffman, George B. (1980) "Adolf von Baeyer and the naming of barbituric acid," Journal of Chemical Education, 57: 222–223.
- ^ Jie Jack Li, Laughing Gas, Viagra, and Lipitor: The Human Stories Behind the Drugs We Use (Oxford, England: Oxford University Press, 2006), p. 204.
- ^ Alex Nickon, Ernest F. Silversmith, Organic Chemistry: The Name Game: Modern Coined Terms and Their Origins (New York, New York: Pergamon Press, 1987), pp. 133–134.
- ^ Baeyer, Adolf (1863) "Untersuchungen über die Harnsäuregruppe" (Investigations of the uric acid group), Annalen der Chemie, 127: 1–27' 199–236' see especially pages 231–235. Baeyer names barbituric acid on page 3: "Man wird sehen, wie sich diese Materialien in einfachster Weise um die Substanz N2C4O3H4, die ich Barbitursäure nennen will, gruppieren lassen und wie also die Frage nach der Konstitution der Harnsäure und ihrer Derivate auf die Untersuchung dieser Substanz zurückgekehrt ist." (One will see how these materials can be grouped most simply around the substance N2C4O3H4, which I will call "barbituric acid", and thus how the question of the constitution of uric acid and its derivatives is traced back to the investigation of this substance.)
- ^ Baeyer, Adolf (1864) "Untersuchungen über die Harnsäuregruppe" (Investigations of the uric acid group), Annalen der Chemie, 130: 129–175; p. 136.
- ^ Grimaux, Edouard (1879) "Synthèse des dérivés uriques de la série de l'alloxane" (Synthesis of uric derivatives of the alloxan series), Bulletin de la Société chimique de Paris, 2nd series, 31: 146–149.
- ^ Michael, Arthur (1887) "Ueber neue Reactionen mit Natriumacetessig- und Natriummalonsäureäthern" (On new reactions with sodium acetoacetic- and sodium malonic acid esters), Journal für Praktische Chemie, 2nd series, 35: 449-459; p. 456.
- ^ J. B. Dickey & A. R. Gray (1943). "Barbituric acid". Organic Syntheses; Collected Volumes, vol. 2, p. 60.
- ^ López-Muñoz, Francisco; Ucha-Udabe, Ronaldo; Alamo, Cecilio (December 2005). "The history of barbiturates a century after their clinical introduction". Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 1 (4): 329–343. ISSN 1176-6328. PMC 2424120. PMID 18568113.
- ^ U.S. patent 3,461,461
- ^ Boyd E M, Pearl M. Can nalorphine hydrochloride prevent respiratory depression and death from overdose of barbiturates?[J]. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 1955, 73(1):35-8.
- ^ Koppanyi T, Fazekas J F. Acute Barbiturate Poisoning Analysis and Evaluation of Current Therapy[J]. American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 1950, 220(5):559-576.
- ^ Shulman A, Shaw F H, Cass N M, et al. A New Treatment of Barbiturate Intoxication[J]. British Medical Journal, 1955, 1(4924):1238-44.
- ^ Bateman C H. Barbiturate Poisoning[J]. Lancet, 1963, 282(7303):357.
- ^ Title 21, Subchapter I, Part B §812. Schedules of controlled substances https://www.deadiversion.usdoj.gov/21cfr/21usc/812.htm Archived 2021-11-04 at the Wayback Machine
External links
[edit]- Mahmudov, K.T.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Maharramov, A.M.; Kurbanova, M.M.; Gurbanov, A.V.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. (2014). "Barbituric acids as a useful tool for the construction of coordination and supramolecular compounds". Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 265: 1–37. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.002.